How To Fatten up A Dog?
Last updated: March 28, 2024

Summary
- Rule out health issues with a vet before fattening your dog.
- Weight gain causes: Low calorie intake, health conditions, high activity, stress/anxiety, puppy/senior age.
- Diet tips: High-calorie food, calorie-dense mix-ins, smaller frequent meals, limit low-calorie fillers, make food appealing.
- Additional tips: Encourage exercise, minimize stress, provide enough water, address dental issues, consider supplements, take it slow.
- Monitor progress: Weekly weigh-ins, regular body condition checks, stick to calorie targets, note any side effects, schedule vet visits.
A dog's weight speaks volumes about their health. However, determining ideal canine weights poses head-scratching questions for many owners. Is my pooch portly or pleasantly plump? Does that prominent ribcage signal cause for concern?
When a weight problem emerges, anxiety clouds judgment on proper fixes. Rapid interventions may tax tiny tummies. Yet letting pounds slide courts trouble.
This article explores proper protocols for assessing and addressing underweight dogs. You'll uncover potential health conditions causing wasted waistlines. You will also learn about the best methods you can adopt to help your puppy gain some weight.
Understanding Why Your Dog May Be Underweight

There are several potential reasons why a dog may be underweight or fail to gain weight appropriately. The following are common causes:
Insufficient Calorie Intake
If a dog is not receiving enough calories on a daily basis to meet their energy needs, they will start to lose weight. Factors like a low appetite, digestive issues preventing nutrient absorption, or an underlying medical condition can lead to this calorie deficit.
In cases where a dog's appetite is suppressed, it's important to understand how long they can go without eating before it becomes a cause for concern.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain illnesses and diseases affecting a dog's appetite, ability to digest food or metabolic processes can result in undesirable weight loss. These include:
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Dental disease or mouth pain
- Cancer
- Kidney, liver, or thyroid dysfunction
- Diabetes
- Parasites
- Mange
In some cases, food allergies can also be a culprit behind weight loss. If you suspect your dog might have food allergies, consulting a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and exploring nutritional solutions like those offered in the best dog food with allergies can be beneficial.
High Activity Levels

Work dogs, sporting dogs and other highly active breeds have increased caloric needs. If their diet does not support their lifestyle, they can become underweight.
Stress, Anxiety, or Depression
Mental health issues in dogs can manifest in a loss of appetite and failure to thrive. Situations causing stress like rehoming, grief or insecure attachment can negatively impact weight.
Puppy or Senior Dog
Growing puppies need ample calories to fuel growth and development. Meanwhile, senior dogs often experience lowered metabolism and activity levels. Their nutritional needs change over time.
Consulting with a veterinarian to diagnose and address any underlying medical conditions is an important first step before attempting to intentionally fatten up an underweight dog. Only once illness is ruled out should specific weight gain strategies be implemented under professional guidance.
Dietary Changes To Help Fatten Up Your Dog

The primary goal when attempting to fatten up an underweight dog is to increase their overall calorie intake. There are several diet-based strategies to help pack on healthy weight:
Switch to a High-Calorie Dog Food
Veterinary hospitals, pet stores and online retailers offer specialty weight gain dog food formulas richer in protein, fat, complex carbs, and calories compared to regular maintenance diets.
Explore curated selections and in-depth analyses of these formulas in essential elements for building a balanced canine diet to identify the perfect food choice for your dog's specific needs and preferences.
Incorporate Calorie-Dense Mix-ins
Some healthy, natural add-ins to boost calories include cooked eggs, full-fat yogurt, cheese, salmon or meat-based oils, unsweetened peanut butter, etc.
Make sure you incorporate these foods into your puppy's daily meals to help him/her gain weight.
Feed Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Instead of one or two large meals, break the day’s food into 3-4 smaller servings. This helps regulate metabolism and prevents stomach upset.
Limit Low-Calorie Fillers
Replace fruits and vegetables used as snacks or meal mix-ins with more energy-dense options so your dog feels full from calories instead of bulk or volume.
Make Food More Appealing
Warming canned food to room or body temperature, adding tantalizing meat juices, or sprinkling on a small amount of Parmesan cheese can make mealtime more enticing. Allow slight table scraps.
Work closely with your veterinarian to determine an optimal calorie target and supervision through scheduled weight checks. Gradual increases are safer and help minimize digestive upset or the risk of overfeeding.
Additional Strategies To Support Weight Gain
While an increased calorie diet is the cornerstone of healthy weight gain, certain additional tactics can facilitate the process:

Encourage Physical Activity
Ensuring adequate exercise will help stimulate your dog's appetite while building muscle mass, not just fat.
Bear in mind that the physical activity must be tailored to your dog's capability and age. For instance, puppies and senior dogs should not overexert.
Minimize Stress
Anxiety, insecure attachment, lack of routine, or introduction of new pets may interfere with weight goals.
To minimize the stress related to all those issues, try to stick to regular schedules, give affection and even use calming aids if needed.
Provide Adequate Hydration
Getting sufficient water keeps digestion on track and prevents dehydration from excess calories. Make clean water continuously available.
Additionally, consider adding broths or low-sodium stocks to encourage drinking.
Address Any Dental Issues
Ensure there is no mouth pain or poor dentition preventing chewing or causing reduced food drive. After that, schedule a veterinary dental cleaning if needed.
Discuss Supplements
In some cases, probiotic, enzyme, or vitamin supplements support nutrition absorption and metabolism.
It is recommended to consult your veterinarian before starting any new regimen.
Take It Slow
Gradual weekly weight gain allows the body to adjust, as opposed to sudden excess intake potentially overwhelming the system or turning straight to fat. Patience facilitates healthy progress.
Continue monitoring weight, body condition score, and health status with scheduled veterinary oversight until the goal weight is reached. Adjust recommendations over time based on how your individual dog responds.
Monitoring Your Dog's Progress
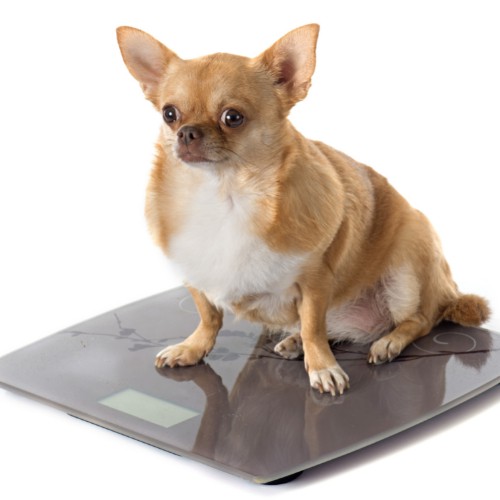

The journey to healthy weight gain requires diligent monitoring between veterinary visits to ensure your dog is improving at an appropriate pace without overdoing it. Below are key tracking tips:
Weigh Your Dog Weekly
Use the same scale at the same time of day each week. Write the weights down to monitor trends over time. Expect to see gradual increases instead of rapid spikes.
Assess Body Condition Score Regularly
Hands-on rib checks coupled with visual waistline and abdomen tuck evaluations let you physically gauge improvements in your dog's body condition versus just the number on the scale.
Stick to Recommended Calorie Targets
If weight gain seems too rapid, level off calorie intake without sacrificing nutrition. It is easier for long-term success to undershoot and increase gradually if needed.
Note Any Adverse Effects
While unusual, contact your vet if you notice signs of digestive issues, food intolerance, lethargy, or other discomfort as you transition your dog to a higher-calorie diet.
Schedule Progress Veterinary Visits
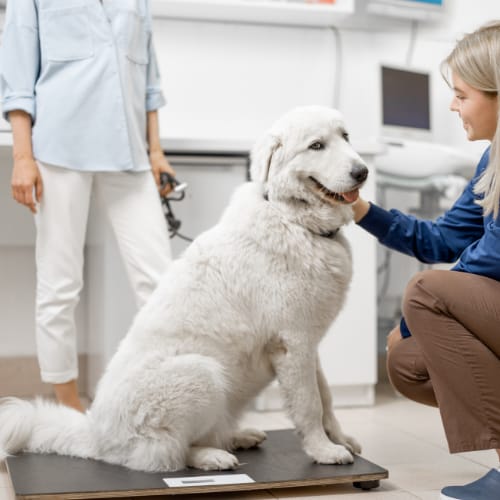

Your vet will want to evaluate weight metrics, diet changes and overall health at regular intervals. Plan follow-ups accordingly to determine if and when adjustments become necessary.
Be proud of the progress made while staying patient through setbacks. Consistency is vital when helping fatten up an underweight dog to reach optimal fitness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some common questions that arise when attempting to fatten up an underweight dog.
What if My Dog is a Picky Eater?
Start by trying different protein sources and commercial weight gain diets until you find one they fancy. Warming food, adding mix-ins, and exercising before meals can stimulate appetite.
Consider adding ketchup, honey, broths, or gravies to entice interest if approved by your veterinarian.
How Many Extra Calories Does My Dog Need Per Day?
There is no universal number - your vet will calculate an ideal daily calorie target based on your individual dog’s age, breed, activity level, and degree of underweight status.
Typically, an extra 200-400 calories per day leads to a safe 1⁄2 to 1 pound weight gain per week.
What is the Best Type of Food for Weight Gain?
Look for a high-quality commercial dog food designed specifically for weight gain, which will have increased protein, fat and fiber levels. Some top options are Purina Pro Plan Veterinary Diets EN Gastroenteric, Hill’s Prescription Diet Metabolic Advanced Weight Solution, or Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Gastrointestinal High Energy.
How Long Will It Take My Dog to Reach a Healthy Weight?
The amount of time depends greatly on the dog and the magnitude of weight that needs to be gained to attain ideal body condition. Most veterinarians recommend shooting for no more than 3-5% increase in body weight per week, so gaining 10 pounds may reasonably take 8-10 weeks at that pace. Go slowly and steadily.
Final Thoughts
The keys to successfully fattening up an underweight dog are veterinary guidance, incremental diet changes allowing adjustment, and monitoring progress carefully. Address any underlying illness first before strategizing weight gain.
If your veterinarian confirms weight gain is needed for health, expect visible improvements in energy, stamina, skin/coat condition, healthy weight management, and potentially extended lifespan from lower disease risk over time if nutritional protocols are followed.
We hope this guide managed to answer all your lingering questions about the topic at hand, and that you will be able to put together a plan to help your puppy gain weight safely. If you have questions or comments, please contact us.






